Investigation of predictive models for monitoring atmospheric pollutants and minimization strategies in sanitation systems: AtmosphAIr 2.0.
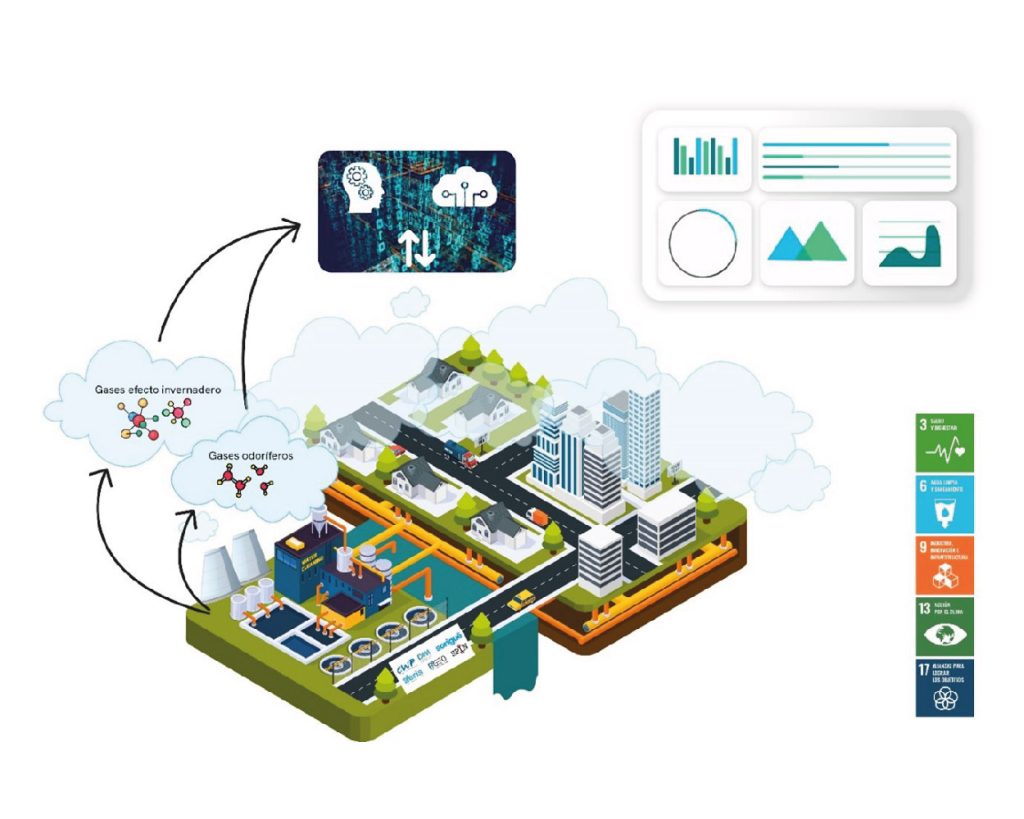
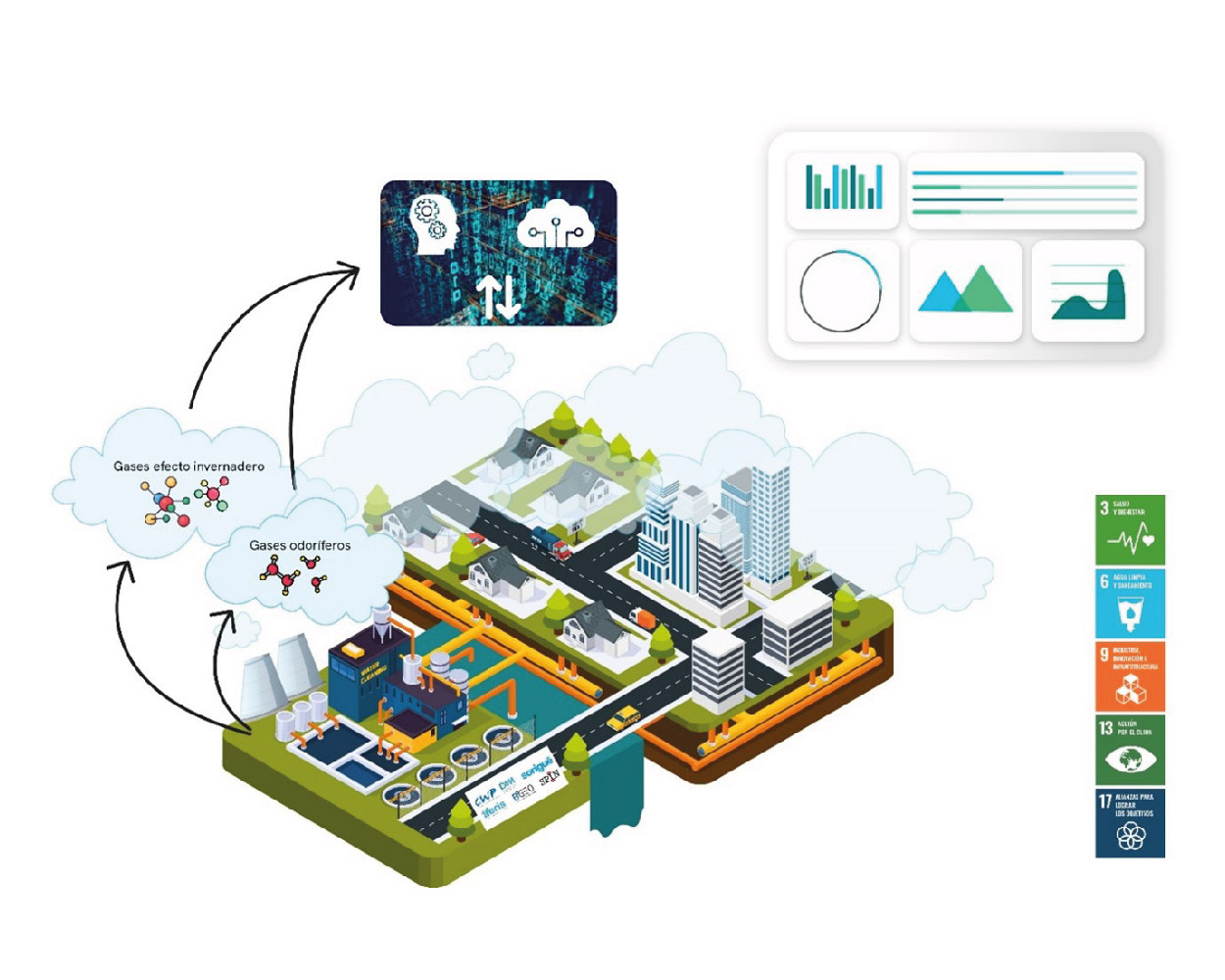
- The AtmosphAIr2.0 project aims to investigate in detail the process of odoriferous and greenhouse gas generation in wastewater treatment plants (EDARs) and improve its prediction using Artificial Intelligence tools.
- The project is a continuation of a previous initiative, AtmosphAIr, which had achieved promising preliminary results in both the detection and prediction of the formation of odoriferous and greenhouse gases.
This project, the second phase of the precursor project AtmosphAIr, seeks to expand knowledge about the patterns and causes of greenhouse gas and odoriferous gas formation in water treatment infrastructures, as well as to improve the prediction of how and why these gases form using artificial intelligence tools developed in the first phase.
Building on the results of the previous phase and utilizing new time series data, the project aims to develop a future digital platform to anticipate and prevent the generation and dispersion of odoriferous and/or greenhouse gases. The ultimate goal of the project is to equip wastewater treatment plant (EDAR) management entities with control tools to optimize plant operations and minimize environmental impact.
The project is being carried out at the Torredembarra (Tarragona) and Montornès del Vallès (Barcelona) wastewater treatment plants, along with their associated sanitation networks. It is promoted by the companies AERIS, BGEO, SPIN, DAM, and SORIGUÉ, and coordinated by the CWP. The project is co-financed by the Ministry of Industry, Trade, and Tourism (MINCOTUR) under the 2023 call for Innovative Business Groups (AEIs) as part of the Next Generation funds and the Recovery, Transformation, and Resilience Plan. Project code: AEI-010500-2023-33.